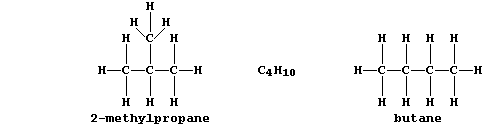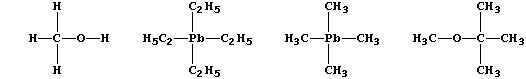ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: ALKANES
All chain alkanes belong to an homologous series which has the general
formula CnH2n+2; the Table shows some data for typical homologues. In
industry, most of these saturated hydrocarbons are usually obtained by
the fractional distillation of either petroleum oil or the products of
cracking; they are used mainly as fuels and as industrial solvents.
Systematic name |
Molecular formula
(state at 25°C) |
Boiling
pt. / °C |
Heat of combustion
(DH) / kJ mol-¹ |
Ethane |
C2H6 (g) |
-89 |
-1560 |
Propane |
C3H8 (g) |
-42 |
-2220 |
2-Methylpropane |
C4H10 (g) |
-11.5 |
-2875 |
Butane |
C4H10 (g) |
-0.5 |
-2880 |
Octane |
C8H18 (l) |
+126 |
-5520 |
Eicosane |
C20H42 (s) |
+343 |
-13440 |
1. The female tiger moth (Homomelia imaculata) signifies its presence
to the males by secreting minute quantities of a sex attractant. This
example of an insect 'pheromone' is a 2-methyl branched-chain alkane
with a molecular formula of C18H38; the straight-chain isomer does not
elicit a response. Noting the structural difference between butane and
2-methylpropane, draw the structural formula of this pheromone. _______
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
2. Natural gas, which is mostly methane, is a non-renewable resource.
However, fermentation of sewage gives a mixture of methane and carbon
dioxide known as 'biogas'; the following symbol equation summarizes one
biological process that occurs in fermenters and in landfill sites:
Methanobacteria enzymes
C6H12O6(aq) —————————————————————® 3CH4(g) + 3CO2(g) -DE
(a) State briefly why both methane and carbon dioxide are considered to
be 'greenhouse' gases. ________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[1]
(b) Biogas can be used as a fuel, because some of its chemical energy
is transduced to 'high-grade' heat energy when the methane burns:
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) —————————————————————® CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) -DH
The heat of combustion for a straight-chain alkane can be calculated
from the linearly proportional relationship DH = k × n + c, where: k
is a proportionality constant, with a value of -660 kJ mol-¹; n is the
number of carbons; and c is a constant, with a value of -240 kJ mol-¹.
Use this relationship to calculate the heat of combustion (DH) for:
Methane (b.pt. -164°C) ________________________________________________
Pentane (b.pt. +36°C) _________________________________________________
[3]
3. Petrol is a blended mixture of several branched- and straight-chain
alkanes, including heptane [C7H16(l)], octane, and nonane [C9H20(l)].
The symbol equation for the complete combustion of gaseous heptane is:
2C7H16(g) + 22O2(g) —————————® 14CO2(g) + 16H2O(g)
Incomplete combustion will occur, however, if there is not sufficient
atmospheric oxygen available; e.g.,
2C7H16(g) + 15O2(g) —————————® 14CO(g) + 16H2O(g)
(a) Construct a symbol equation for the complete combustion of octane.
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
(b) The combustion properties of petrol are improved by additives such
as methanol [CH3OH(l)], tetraethyllead [(C2H5)4Pb(l)], tetramethyllead
[(CH3)4Pb(l)], and methoxy-2-methylpropane [CH3OC(CH3)3(l)].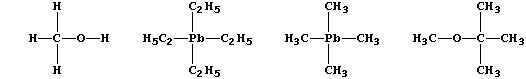
Construct a symbol equation for the synthesis of tetraethyllead, which
is manufactured by heating a mixture of sodium, lead, and chloroethane.
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
Suggest a suitable solvent for tetraethyllead; this covalent compound
is immiscible with water. _____________________________________________
[1]
Tetraethyllead burns to form lead(IV) oxide, carbon dioxide, and steam.
Construct the symbol equation for this combustion reaction. ___________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
Suggest one advantage in using methoxy-2-methylpropane as an additive.
_______________________________________________________________________
[1]
(c) Pollutants emitted from a vehicle exhaust include carbon monoxide,
nitrogen oxides, and unburned hydrocarbons; these are converted into
safer emissions if the exhaust is fitted with a 'catalytic convertor':
Pt-Rh / D
2CO(g) + 2NO(g) —————————® CO2(g) + N2(g)
Describe one biological effect of carbon monoxide. ____________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
State three effects of nitrogen oxide pollutants. _____________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[3]
Vehicles with convertors must use unleaded-petrol to minimize 'catalyst
poisoning'. Explain how lead compounds inhibit such catalysts. ________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
4. Candlewax is usually a mixture of organic compounds from different
homologous series, including alkanes such as eicosane and triacontane
(C30H62). Suggest one technique which could be used to show that wax is
not a pure compound. __________________________________________________
[1]
Products formed from the incomplete combustion of wax include soot and
carbon monoxide. Soot is largely a non-crystalline (or amorphous) form
of which element? _____________________________________________________
[1]
Dr. R. Peters Next Contents' List