METALS: ALUMINIUM & ZINC COMPOUNDS
Both aluminium and zinc are used extensively in industry, either as the
pure metals or in alloys. By contrast, compounds of these metals have
found considerably fewer commercial applications, but some are used;
e.g., as rodenticides, in paint pigments, as fire retardents, and in
water purification [zinc phosphide, zinc oxide, aluminium hydroxide,
and aluminium sulfate, respectively.]
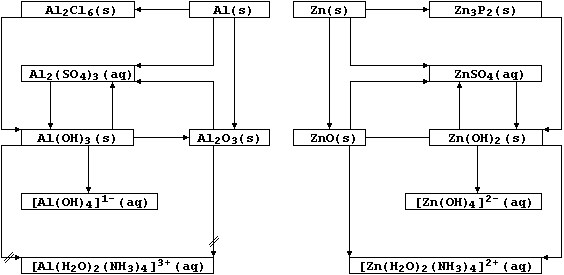
Aluminium and zinc form compounds with the metal ions in different
oxidation states [Al(III) and Zn(II)]. This difference may partially
explain why enzymes containing zinc - but not aluminium - are essential
to all biological species; particularly ubiquitous are the carbonic
anhydrases and the carboxypeptidases, which are involved in respiration
and protein hydrolysis, respectively. Nevertheless, clearly reflecting
their near-adjacent positions in the reactivity series, the chemistry
of these metals and their compounds show noteworthy similarities - as
these schemes perhaps over-emphasize?
[.. K > Ca > Na > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Sn > Pb > (H) > Cu > Hg > Ag ..]
1. Aluminium and zinc are both used to test for the presence of
nitrate ions. Thus, heating an alkaline solution containing nitrate
ions with either powdered aluminium or zinc results in the evolution of
an alkaline gas (ammonia); the symbol equations for such reactions are:
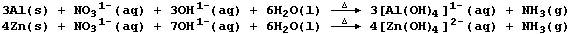
Suggest why the nitrate ion is considered to be reduced in this test.
_______________________________________________________________________
[1]
2. Aluminium chloride and zinc phosphide are both prepared directly by
heating their respective elements. Construct the symbol equation for
the synthesis of each of these covalently bonded compounds. ___________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
3. Zinc phosphide hydrolyzes in water to give the extremely toxic gas
phosphine: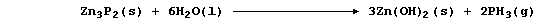
A number of aluminium compounds are hydrolyzed in a similar manner to
zinc phosphide. Predict the name and formula of the gas or solution
produced when each of the following are added separately to water.
Aluminium chloride (Al2Cl6) ___________________________________________
Aluminium nitride (AlN) _______________________________________________
Aluminium carbide (Al4C3) _____________________________________________
[6]
4. Zinc oxide is thermochromic; i.e., it changes colour with changes
in temperature:
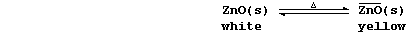
Suggest one reason why both processes should be considered as chemical
changes. ______________________________________________________________
[1]
5. Flammable polymers, such as poly(ethene) and poly(chloroethene),
are used extensively in furnishings; to reduce their potential as fire
hazards, flame retardents are often added to these materials. Construct
the symbol equation, complete with a qualitative indication of the heat
energy change, for the thermal decomposition of aluminium hydroxide.
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
Suggest one way aluminium hydroxide acts as a fire retardent. _________
_______________________________________________________________________
[1]
6. As the reaction schemes show, the oxides and hydroxides of zinc and
aluminium react with both acids and bases; i.e., they are amphoteric
(cf. amphibians). Typical reactions which exemplify the amphoteric
character of aluminium oxide are summarized by this pair of equations: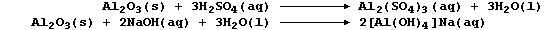
Complete the following symbol equations, which will summarize reactions
exemplifying the similarly amphoteric character of zinc oxide:
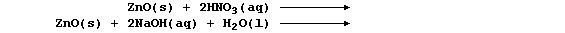
7. Aluminium hydroxide is used as a coagulating agent in helping to
remove suspended solids from domestic water supplies. Thus, the careful
addition of calcium hydroxide to tanks of water containing aluminium
sulfate results in the formation of aluminium hydroxide - which, as a
gelatinous precipitate, is ideal for trapping suspended solids:
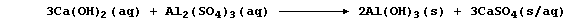
This symbol equation reveals two precipitation reactions. Construct a
net ionic equation for each of these reactions. _______________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
Suggest one reason why the quantity of calcium hydroxide must be very
carefully controlled, apart from preventing the aluminium hydroxide
redissolving. _________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[1]
In view of a possible connection between aluminium ions and Alzheimer's
disease (which causes premature senile dementia), suggest one compound
which might be a suitable alternative to aluminium hydroxide as the
coagulating agent. ____________________________________________________
[1]
8. Aqueous ammonia is one reagent used to distinguish between aqueous
solutions of aluminium and zinc ions. Thus, the dropwise addition of
aqueous ammonia to a solution containing aluminium ions results in the
formation of a white precipitate, Al(OH)3, which does not redissolve
in excess reagent. However, although the dropwise addition of aqueous
ammonia to a solution containing zinc ions similarly results in the
formation of a white precipitate, Zn(OH)2, this does redissolve in
excess reagent to form a solution containing a soluble tetraamminezinc
ion, [Zn(H2O)2(NH3)4]2+(aq). Suggest one method of distinguishing
between solid samples of aluminium oxide and zinc oxide, apart from
their reactions with aqueous ammonia. _________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
Dr. R. Peters Next Contents' List