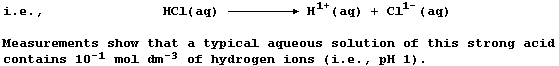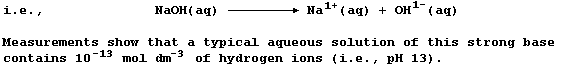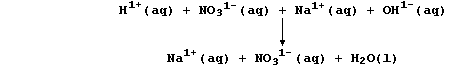SELECTED PRINCIPLES: ACIDS & BASES (1)
Certain definitions, which are intentionally narrow, will be useful in
this introduction to acid-base chemistry. First, acids are substances
which produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in water. Second, bases are
substances which accept hydrogen ions (e.g., the hydroxides, oxides,
sulfides, hydrogencarbonates, and carbonates of metals); those which
are soluble in water are known as alkalis. Third, salts are ionic
compounds which contain ions other than hydrogen, hydroxide, or oxide.
And finally, neutralization is the reaction between an acid and a base.
When hydrogen chloride is dissolved in an organic solvent, the solution
formed does not conduct an electric current - indicating the absence of
free-moving ions. By contrast, when this gas is dissolved in water,
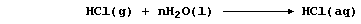
the aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid formed conducts an electric
current strongly, because this 'strong' acid is completely dissociated;
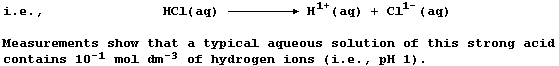
When sodium hydroxide is dissolved in water,
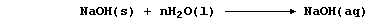
the aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide formed conducts an electric
current strongly, because this 'strong' base is completely dissociated;
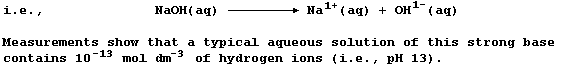
The symbol equation for the neutralization reaction between aqueous
solutions of nitric acid and sodium hydroxide is:
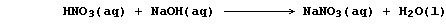
Because the reactants are completely dissociated, a better perspective
of this reaction is gained by constructing an ionic equation;
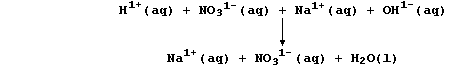
Those ions that are not involved in the overall reaction, here aqueous
sodium and nitrate, are referred to as 'spectator' ions; and, so as to
focus on the change that actually occurs in this neutralization, a net
ionic equation can be written; i.e.,
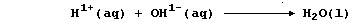
The measured heat energy change (DH) for this (exothermic) reaction is
-56 kJ mol-¹.
1. The symbol equation for the neutralization reaction between aqueous
solutions of sulfuric acid and potassium hydroxide is:
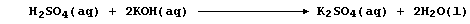
(a) State the spectator ions in this reaction. ________________________
[2]
(b) Construct the net ionic equation for this reaction. _______________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
2. In humans, both pancreatic juice and bile are rich in hydrogen-
carbonate ions; these neutralize the acidity of the chyme flowing from
the stomach, as well as provide the slightly alkaline pH required for
optimal activity of the pancreatic enzymes. The symbol equation for the
neutralization reaction, which occurs in the duodenum, is: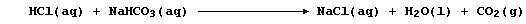
(a) Construct the ionic equation for this reaction. ___________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
(b) Describe one other rôle of bile in digestion. _____________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
3. Acidic gases are released into the atmosphere when fossil fuels are
burnt. The condensation of atmospheric water vapour containing these
gases, and others formed in the atmosphere, leads to the precipitation
of 'acid rain' - which is a mixture of several acids. Depending on the
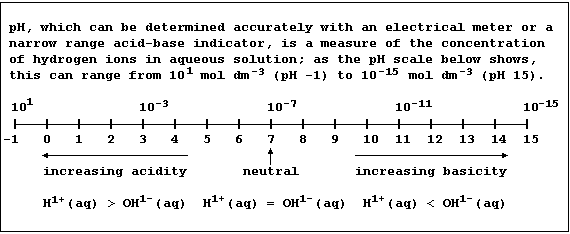
weather conditions and location, this rain or snow can have a pH of
between 2.2 and 5.5: by contrast, unpolluted rainwater has a pH of 5.6.
(a) State the percentage increase in hydrogen ions of rainwater with a
pH of 2.6 compared to that with a pH of 5.6. __________________________
[1]
(b) Hydrated metal ions usually enter living cells by diffusion across
semi-permeable membranes. In unpolluted environments, the concentration
of most toxic metal ions is very low because these ions are 'locked-up'
in insoluble compounds [e.g., aluminium oxide, cadmium(II) carbonate,
lead(II) sulfide, and mercury(II) sulfide]: but, such compounds react
with the components of acid deposition - as a result, the concentration
of toxic hydrated ions increases markedly in polluted environments.
Contruct the symbol equation for the neutralization reaction between:
Dilute nitric acid and aluminium oxide ________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
Dilute nitric acid and lead(II) sulfide _______________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[4]
(c) Acidified soils are often treated with either quicklime, CaO(s), or
slaked lime, whereas acidified lakes are usually treated with powdered
limestone. Construct a symbol equation for the neutralization reaction
between:
Dilute sulfuric acid and quicklime ____________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
Dilute sulfuric acid and limestone ____________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[4]
(d) Saprotrophic organisms are vitally important in the recycling of
chemical energy and nutrient ions within the biosphere. Suggest and
explain one reason why the growth and reproductive rates of saprotrophs
usually decrease in acidic environments. ______________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
Dr. R. Peters Next Contents' List