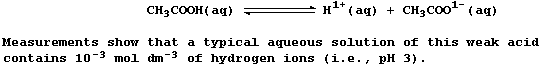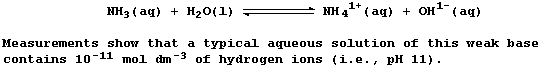SELECTED PRINCIPLES: ACIDS & BASES (2)
When ethanoic acid is dissolved in an organic solvent, the solution
formed does not conduct an electric current - indicating the absence of
free-moving ions. By contrast, when this liquid is dissolved in water,
the aqueous solution of ethanoic acid formed conducts an electric
current weakly, because this 'weak' acid is partially dissociated;
i.e., the position of the following equilibrium lies far to the left:
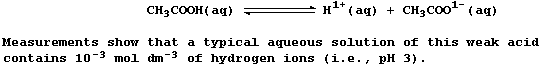
Water is often considered to be a purely covalent compound. However,
even after extensive purification by repeated distillation, the purest
sample of water still conducts an electric current very weakly. The
explanation for this observation is that water undergoes very slight
dissociation (or ionization); the position of the following equilibrium
lies almost completely to the left:

When ammonia gas is dissolved in water,
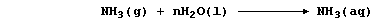
the aqueous solution of ammonia formed conducts an electric current
weakly, because this 'weak' base is partially dissociated; i.e., the
position of the following equilibrium lies far to the left:
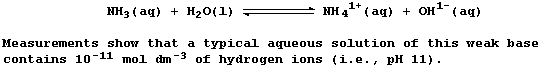
The descriptive terms 'strong' and 'weak', used in reference to acids
and bases, are simply a qualitative measure of the extent of ionization
or dissociation in water; they do not refer to the concentration of
substance: so, oxymoronic phrases such as 'concentrated weak acid' and
'dilute strong base' are perfectly acceptable - as this Table reveals.
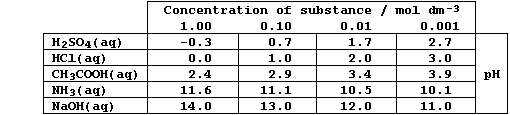

1. Collisions between free-moving ions in aqueous solutions usually
occur so frequently that most ionic reactions, including neutralization
and precipitation, are immeasurably fast. The 'instantaneous' character
of neutralization allows various hypotheses to be investigated; e.g.,
'The speed (S) at which aqueous ethanoic acid 'ice-cubes' dissolve in
aqueous sodium hydroxide is in direct proportion to their surface area
(A); i.e., S = k × A'.
(a) Construct the symbol equation for the neutralization reaction
between aqueous solutions of ethanoic acid and sodium hydroxide. ______
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
State the spectator ions in this reaction. ____________________________
[2]
(b) Suggest three independent variables which must be measured and held
constant in order to isolate the independent variable of surface area.
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[3]
(c) What type of substance would be used to determine that an ethanoic
acid 'ice-cube' had completely dissolved in aqueous sodium hydroxide?
_______________________________________________________________________
[1]
(d) Calculate the total surface of one 'ice-cube' if the surface area
of one face is 4 cm². _________________________________________________
[1]
What physical property of ice results in its effective surface area in
contact with an aqueous solution being less than that calculated? _____
_______________________________________________________________________
[1]
(e) Calculate the volume of one 'ice-cube' if the surface area of one
face is 4 cm². ________________________________________________________
[1]
If the concentration of the aqueous ethanoic acid used to make the
'ice-cubes' is 0.125 mol dm-³, calculate the number of moles of acid in
each 'ice-cube'. ______________________________________________________
[2]
2. Despite the abundance of atmospheric dinitrogen, the availability
of usable nitrogen is normally the most important factor limiting plant
growth: so, to sustain or increase crop yields, farmers use artificial
nitrogenous fertilizers. The manufacture of these compounds is typified
by that of ammonium hydrogenphosphate; this involves the neutralization
reaction between aqueous solutions of phosphoric acid and ammonia,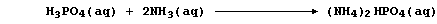
followed by the controlled evaporation of excess water,
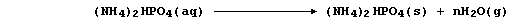
(a) Suggest one reason why the evaporation of an aqueous solution of an
ammonium salt must be carefully controlled. ___________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[1]
(b) Complete this description of one method of preparing crystals of
ammonium hydrogenphosphate. "Wearing safety glasses, transfer 20.0 cm³
of aqueous ammonia (1.00 mol dm-³) to an insulated conical flask, using
a pipette and safety-______; then measure the starting temperature. Add
rapidly _________ of aqueous phosphoric acid (1.00 mol dm-³), using a
a burette; then measure the final temperature of the reaction mixture.
Evaporate this solution, using a ___________________, until crystals
appear; then leave the crystalline mixture to dry at room temperature."
[3]
(c) Suggest one reason why autotrophic organisms require a source of
phosphate. ____________________________________________________________
[1]
Dr. R. Peters Next Contents' List