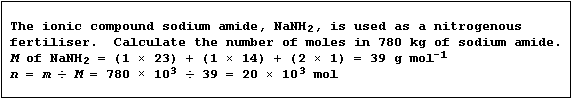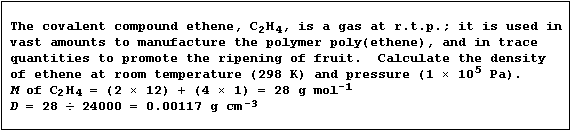REFERENCE SECTION: INTRODUCTION - CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS (2)
Molar Mass (M)
The molar mass (M) of a substance has the same numerical value as its
relative atomic or molecular mass, but has the units g mol-¹.

Masses into Moles
The conversion of masses into moles requires the use of this equation:
Number of moles (n) of substance = Mass (m) ÷ Molar mass (M)
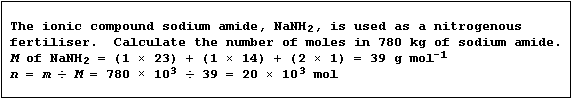
Moles into Masses
The conversion of moles into masses requires the use of this equation:
Mass (m) of substance = Number of moles (n) × Molar mass (M)

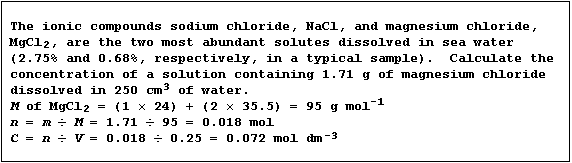
Concentration of a Solution
The concentration (C) of a solution, expressed as mol dm-³, is the
number of moles (n) of solute dissolved in a volume (V) of one cubic
decimetre of solvent; this quantity is calculated using this equation:
Conc. (C) of soln. = No. of moles (n) of solute ÷ Vol. (V) of solvent
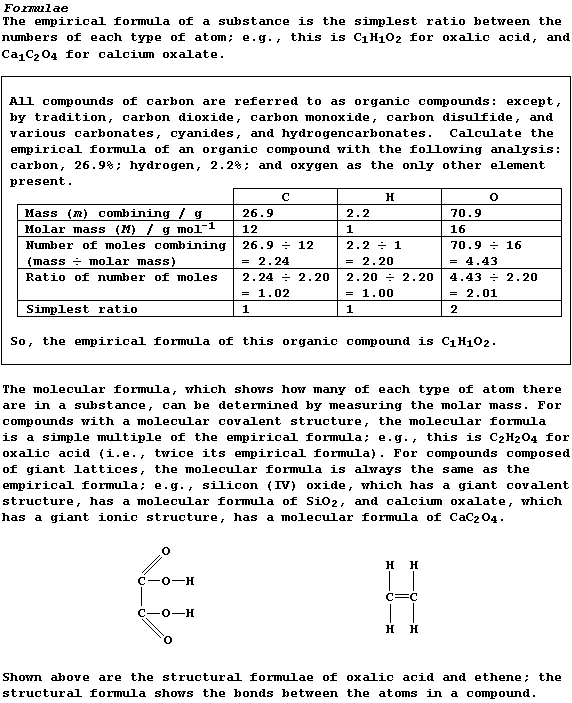
Density of a Gas
The density (D) of a gas, expressed in g cm-³, is the mass (m) of gas
contained in a volume (V) of one cubic centimetre. Because experiments
have shown that 1 mole of any gas, at room temperature and pressure
(r.t.p.), occupies a volume of 24000 cm³, the density of a gas can be
calculated using this equation:
Density (D) of a gas = Molar mass (M) ÷ 24000
Dr. R. Peters Next Contents' List