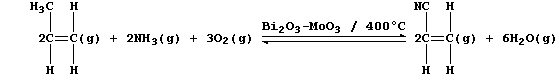METALS: MOLYBDENUM
Molybdenum, a rare element in the Earth's crust (0.002%), is usually
found as a sulfide (e.g., in the ore molybdenite). This transition
metal, which has a very high melting point (2617°C) and a high density
(10.28 g cm-³), forms coloured compounds in several oxidation states
[e.g., Mo(II), Mo(III), and Mo(VI)]. Molybdenum has been shown to be
essential to all living organisms, but its particular importance in
biological chemistry centres on nitrogenase; this molybdenum-containing
enzyme, which is present in nitrogen-fixing bacteria (e.g., Rhizobium),
is involved in the reduction of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia.
[.. K > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Mo > Sn > Pb > (H) > Cu > Hg > Ag ..]
1. The extraction of molybdenum from its ores is very complex, and so
only a simplified summary is presented here:
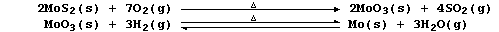
(a) Explain what the double-headed arrow means in the second equation.
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
(b) Suggest a different reductive method of obtaining molybdenum from
molybdenum(VI) oxide. _________________________________________________
[1]
2. Many leguminous plants have evolved symbiotic relationships with
nitrogen-fixing bacteria living in their root nodules; a legume uses
the ammonium ions absorbed from these bacteria to biosynthesize amino
acids, ATP, chlorophylls, and nucleic acids.
(a) Name two legumes. _________________________________________________
(b) Suggest in what form chemical energy is absorbed by these bacteria
from the legume. ______________________________________________________
(c) Cereal farmers will clearly reduce their dependence on artificial
nitrogenous fertilizers if they introduce legumes as 'break crops'.
Explain one disadvantage inherent in the use of such fertilizers. _____
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[5]
3. Industrial nitrogen-fixation is commonly achieved by the Haber
process, which is usually summarized by the following equation: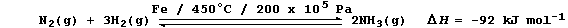
Explain one reason why each of the following conditions speed up the
above reaction - so saving time (and, therefore, money).
Powdered iron _________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
High temperature ______________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
High pressure _________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[6]
4. Molybdenum(VI) oxide is used as a co-catalyst in the industrial
oxidation of a propene and ammonia mixture to propenenitrile.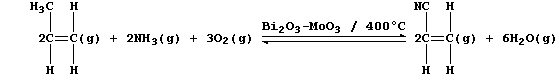
Propenenitrile, better known as acrylonitrile, is the monomer used to
manufacture which polymer? ____________________________________________
[1]
5. Molybdenum's position in the reactivity series can be determined
by measuring potential differences of electrochemical cells; the Table
shows some typical data, together with the electrical conductivities of
the selected metals at ambient temperatures.
Metal(M) |
Al |
Ti |
Cr |
Ga |
In |
Mo |
Rh |
Ir |
Au |
Cell p.d.(Au-M) /V* |
3.16 |
2.71 |
2.24 |
2.06 |
1.84 |
1.70 |
0.74 |
0.34 |
0.00 |
Cond. / MW cm-¹ |
40.0 |
2.6 |
7.9 |
7.4 |
12.5 |
20.0 |
23.2 |
21.2 |
48.8 |
* The data, which have been obtained under standard conditions (25°C;
pH = 0), refer to the oxidation half-reaction M(s) ——® M3+(aq) + 3e- |
(a) Noting that each quantitative dependent variable is a linear scale
on the vertical axis, and that the qualitative independent variable is
shown as separate blocks on the horizontal axis, complete this double
bar-graph of these data.
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
|_| |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| |/|
|_| |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| |/|
|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|
C 3.0_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_60 E
e |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| l
l |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| e
l |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| c
|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| t
p 2.5_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_50 r
o |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| i
t |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| c
e |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| a
n |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| l
t 2.0_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_40
i |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| c
a |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| o
l |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| n
|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| d
d 1.5_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_30 u
i |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| c
f |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| t
f |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| i
e |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| v
r 1.0_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_20 i
e |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| t
n |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| y
c |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|
e |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| /
0.5_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_10
(Au-M) |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_| MW cm-¹
|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|
/ |_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|
|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|
V 0.0_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_|_0
Al Ti
Metal (M)
[7]
(b) Molybdenum may prove attractive as a component of commercial cells,
particularly as it is at least ten times more abundant in the Earth's
crust than cadmium, mercury, or silver (which are used in Ni-Cd, Hg-Zn,
and Ag-Zn cells, respectively). For a specialized application which
required a p.d. of about 1 V, molybdenum could be paired with either of
which two metals? ____________________________________________________
[2]
Dr. R. Peters Next Contents' List