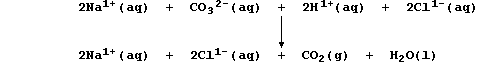METALS: SODIUM COMPOUNDS
The commercial applications of sodium compounds in developed countries
are so numerous that any brief overview has obvious limitations. But,
as a starting point, it does appear appropriate to state that their
extensive use is attributable to the following four aspects. Firstly,
sodium compounds are cheap to manufacture; in part, this reflects the
abundance and accessibility of the raw materials (e.g., sea water and
rock salt both contain sodium chloride). Secondly, sodium compounds are
usually soluble in water and have high thermal stability. Thirdly, in
most applications, it is the chemical properties of the anions which
are important; the sodium cations are usually mere spectators. And
fourthly, sodium cations are (relatively) non-toxic.
1. Brine is a concentrated aqueous solution of sodium chloride. Three
useful products are obtained from the electrolysis of brine, as this
overall symbol equation shows:
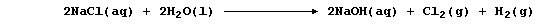
The ionic equations for the reactions occurring at the electrodes are:
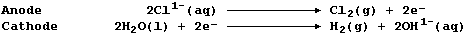
(a) Label this diagram of a (Diaphragm) electrolytic cell with: Cl2(g);
H2(g); NaOH(aq); Saturated brine; Steel cathode; and, Titanium anode.
(b) A typical electrolytic cell used in industry, which operates
continuously at 1.5 kA and 4 V, must have at least five hazard symbols
clearly visible: 'Corrosive' [i.e., NaOH(aq)]; 'Explosive' [H2(g)];
'Highly flammable' [H2(g)]; 'Oxidizing' [Cl2(g)]; and 'Toxic' [Cl2(g].
State three items of safety clothing necessary for workers or visitors.
_______________________________________________________________________
[3]
(c) The diaphragm is selectively permeable, allowing hydroxide (but not
chloride) ions to enter the cathodic compartment. Suggest and explain
one advantage in this selectivity. ____________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
The diaphragm also prevents mixing of the gaseous electrode products,
dihydrogen and dichlorine, which together react explosively. Construct
the symbol equation for this reaction. ________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[1]
(d) Suggest and explain one reason why electrodes made of iron would be
unsuitable. ___________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
2. Aqueous sodium carbonate neutralizes aqueous hydrochloric acid:
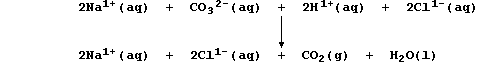
As this ionic equation shows, it is the carbonate (and hydrogen) ions
which are the reactants: the sodium (and chloride) ions are spectators.
Construct a similar ionic equation for the precipitation reaction
between aqueous solutions of sodium hydroxide and iron(II) sulfate.
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
3. Sodium carbonate is thermally very stable; indeed, it melts before
it decomposes at temperatures above 1000°C: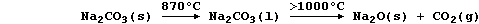
By contrast, sodium hydrogencarbonate is thermally much less stable;
thus, at temperatures above 90°C, it decomposes to give three products.
Construct the symbol equation for this thermal decomposition. _________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
4. The Table below presents one illustrative application for eight
sodium compounds. Complete this Table by inserting the correct formula
from this list: [CH3(CH2)16COO]Na ; NaCl ; NaHCO3 ; NaNH2 ; NaOCl ;
NaOH ; Na2[B2(O2)2(OH)4] ; Na2CO3.
Formula of compound
(Application) |
Property of compound or anion which
is important in specified application |
(Strong base) |
Completely dissociates in water; the hydroxide
ions neutralize aqueous hydrogen ions. |
(Baking powder) |
Partially decomposes when heated; the evolved
carbon dioxide expands, so dough mixtures rise. |
(Fertilizer) |
Hydrolyzes to give ammonia, which is converted
to ammonium ions in the soil: so crops are
provided with a usable source of nitrogen. |
(Glass manufacture) |
Completely decomposes when heated at very high
temperatures; the resulting molten sodium oxide
fuses with other oxides to form glass. |
(Food preservative) |
A concentrated solution, which is non-toxic,
has a low water potential: so water is removed
from pathogenic cells by exo-osmosis across the
semi-permeable membranes. |
(Soap) |
Hydrocarbon chain is lipophilic and ions are
hydrophilic: so has detergent properties, as it
acts as an emulsifying agent for fats and oils. |
(Bleaching agent) |
Partially decomposes when heated to ca. 80°C;
the evolved hydrogen peroxide acts as a bleach. |
(Disinfectant) |
An aqueous solution slowly photolyzes to give
'chlorine water', which is a biocide. |
[8]
5. In Man, sodium ions are required principally for osmoregulation and
for conduction of nerve impulses. State briefly how excess sodium ions
are excreted in this species. _________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
6. Name the only other metal whose compounds are usually non-toxic,
water-soluble, thermally-stable, and cheap to manufacture. ____________
[1]
Dr. R. Peters Next Contents' List