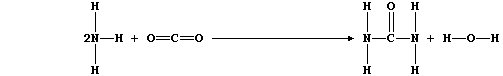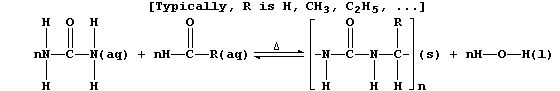ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: UREA
Urea, which is correctly known as carboxamide, has the distinction of
being the first organic compound to have been made in a laboratory
(1828); it is the main nitrogenous excretion product of most mammals.
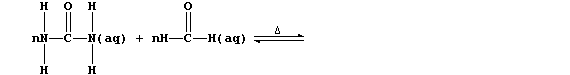
1. Urea is manufactured from ammonia and carbon dioxide;
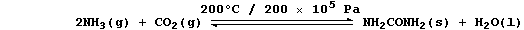
The equation for this condensation reaction can be written as:
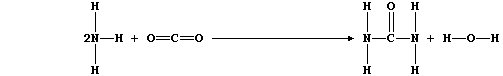
(a) Complete this first Table by inserting the correct numbers of bonds
broken and formed.
Bonds broken |
Energy absorbed
/ kJ mol-¹ |
Bonds formed |
Energy released
/ kJ mol-¹ |
N-H |
2334 |
N-H |
1156 |
C=O |
1490 |
C=O |
745 |
|
|
C-N |
558 |
|
|
O-H |
926 |
Total = 3824 |
Total = 3785 |
[2]
(b) Calculate the heat energy change (DH) for the above reaction. _____
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
(c) Carefully explain two reasons why high temperatures are used in the
industrial process. ___________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[4]
2. The nitrogenous fertilizers in commonest use are ammonium salts,
but others are occasionally used; e.g., urea and sodium amide (NaNH2).
(a) Complete this second Table by calculating the molar mass and the
percentage nitrogen of each compound.
Name |
Formula |
M / mol g-¹ |
% Nitrogen |
Ammonium sulfate |
(NH4)2SO4 |
|
|
Ammonium hydrogenphosphate |
(NH4)2HPO4 |
|
|
Ammonium nitrate |
NH4NO3 |
|
|
Urea |
(NH2)2CO |
|
|
[4]
Apart from its higher nitrogen content, suggest one reason why urea is
sometimes preferred to an ammonium salt as a fertilizer. ______________
_______________________________________________________________________
[1]
(b) Various soil micro-organisms secrete urease; this nickel-containing
enzyme catalyzes the conversion of urea to ammonium carbonate in moist
soils. Construct the symbol equation for this reaction. _______________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
Suggest one pollutant which might inhibit the activity of this enzyme.
_______________________________________________________________________
[1]
3. Urea's principal use is as a monomer in the syntheses of various
condensation polymers that are thermosetting materials (i.e., they do
not soften on heating). One of the many versatile reaction schemes used
is summarized below:
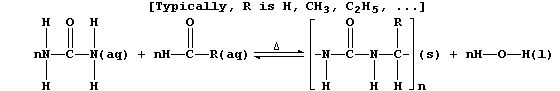
(a) Complete the equation below, which summarizes the conditions used
to prepare the 'parent' polymer (i.e., R = H).
[2]
(b) In contrast to addition polymerization, condensation polymerization
is an endothermic reaction; so, in principle, condensation polymers
should be readily hydrolyzed to their respective monomers. Suggest and
explain one reason why, in practice, synthetic condensation polymers
are usually stable to hydrolysis. _____________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
(c) Naturally occurring condensation polymers include fats, proteins,
carbohydrates, and nucleic acids; their hydrolysis is vitally important
in the transfer and recycling of chemical energy and nutrient ions
between living organisms. For each of the following, name one group of
enzymes involved in their hydrolysis as well as the name of the final
monomeric products.
Carbohydrates _________________________________________________________
[2]
Proteins ______________________________________________________________
[2]
Fats __________________________________________________________________
[3]
(d) Most synthetic condensation polymers, including polyesters such as
Terylene, are thermosetting: but a few, including polyamides such as
Nylon, are thermoplastic (i.e., they soften on heating and harden again
on cooling). By contrast, nearly all synthetic addition polymers are
thermoplastic; the most notable exception is poly(tetrafluoroethene),
popularly known as Teflon, which is thermosetting. Name one addition
polymer, apart from poly(chloroethene), which is a thermoplastic. _____
_______________________________________________________________________
[1]
4. Chemists often use the patterns inherent in the Periodic Table to
justify the syntheses of compounds which should have similar properties
to one already known; e.g., NaCl ('common salt') ——» KCl, NaF, LiI, ...
Suggest the structural formulae of two compounds which might be
expected to show chemical or biological properties similar to urea.
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
[2]
Dr. R. Peters Next Contents' List